728x90
[ 후위 표기식 이란? ]
일반적으로 우리가 사용하는 중위 표기식과 달리 연산자를 뒤쪽에 배치하는 표기식을 의미한다.
(중위 표기식)
1+2*3/2
(후위 표기식)
12+*32/
후위표기식을 구하기 위해 우리는 Stack을 이용한다. 이때문에 컴퓨터는 후위 표기식의 연산속도가 더 빠르다라고 알고 있다.
[ 중위 -> 후위 ]
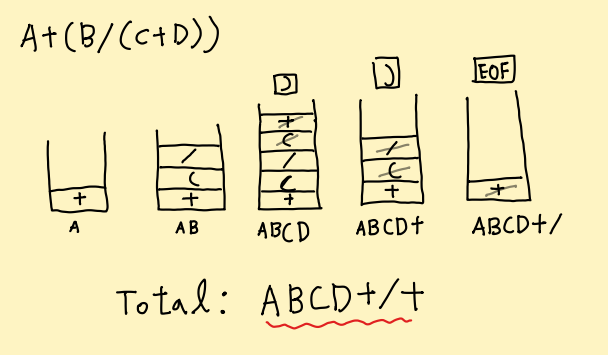
- 우리가 신경써야할 것은 부호를 어떻게 배치하나 이다.
- 피연산자는 순서대로 출력하고, 부호에 의해 괄호 및 우선순위가 결정된다.
[ 원리 ]
- stack에 연산자를 제외한 부호를 넣어준다.
- 만약 *나/가 오게되면 기존에 stack에 있던 같은 우선순위의 부호들(*, /)를 출력 및 pop해주고 자신을 push한다.
- 만약 +나-가 오게되면 이미 자신보다 우선순위가 높은 부호들(*, /)은 없기 때문에 '('가 끝나기 전까지 출력해주고(먼저 들어와있던 부호들) 자신을 출력한다.
- 만약 ')' 가 오게되면 '('가 나오기 전까지 모두 출력해준다.
[ 코드 ]
더보기
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
stack<char> s;
string infix;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
cin >> infix;
for (int i = 0; i < infix.length(); i++) {
if (infix[i] >= 'A' && infix[i] <= 'Z') {
cout << infix[i];
}
if(infix[i] == '*' || infix[i] == '/') { //*나 /인것 순서대로 빼내고 넣기
while (!s.empty() && (s.top() == '*' || s.top() == '/')) {
cout << s.top();
s.pop();
}
s.push(infix[i]);
}
if (infix[i] == '+' || infix[i] == '-') {
while (!s.empty() && s.top() != '(') {
cout << s.top();
s.pop();
}
s.push(infix[i]);
}
if (infix[i] == '(') {
s.push(infix[i]);
}
if (infix[i] == ')') {
while (!s.empty() && s.top() != '(') {
cout << s.top();
s.pop();
}
s.pop(); // ( 제거
}
}
while (!s.empty()) {
cout << s.top();
s.pop();
}
return 0;
}
[ 후위 표기식 답 구하기 ]
BOJ 1935] 후위 표기식2
위에서 구한 후위 표기식의 답을 구해보자.
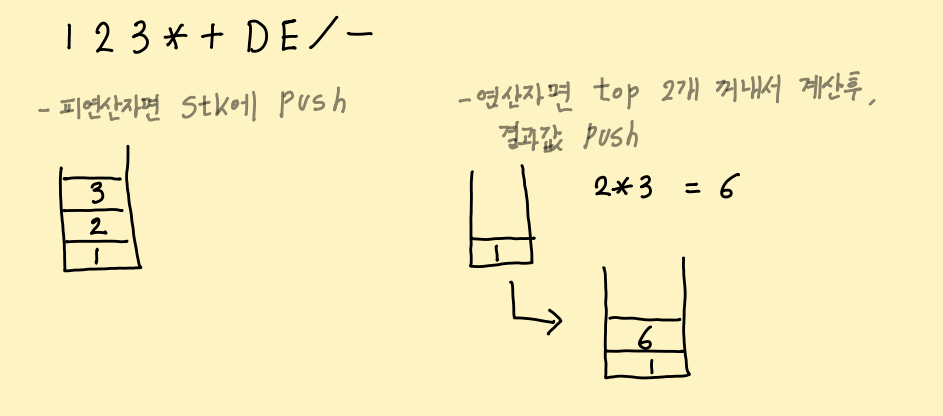
위 과정을 반복하면 끝!
[ 코드 ]
더보기
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
stack<double> s;
int num[27];
string str;
int n;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
cin >> n;
cin >> str;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> num[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if (str[i] >= 'A' && str[i] <= 'Z') {
s.push(num[str[i] - 'A']);
}
else { // 연산자
if (!s.empty()) {
double res;
double b = s.top();
s.pop();
double a = s.top();
s.pop();
if (str[i] == '+') {
res = a + b;
}
else if (str[i] == '-') {
res = a - b;
}
else if (str[i] == '*') {
res = a * b;
}
else if (str[i] == '/') {
res = a / b;
}
s.push(res);
}
}
}
printf("%.2f", s.top());
return 0;
}728x90
'📊알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 시간 복잡도 (0) | 2023.01.06 |
|---|---|
| DP 문제 맛보기 (카드 구매하기 1,2) (0) | 2022.12.19 |
